What you will find on this page: LATEST NEWS; Fossil fuel emissions have stalled; Analysis: Record surge of clean energy in 2024 halts China’s CO2 rise; does the world need hydrogen?; Mapped: global coal trade; Complexity of energy systems (maps); Mapped: Germany’s energy sources (interactive access); Power to the people (video); Unburnable Carbon (report); Stern Commission Review; Garnaut reports; live generation data; fossil fuel subsidies; divestment; how to run a divestment campaign guide; local council divestment guide; US coal plant retirement; oil conventional & unconventional; CSG battle in Australia (videos); CSG battle in Victoria; leasing maps for Victoria; coal projects Victoria
Huge task to decarbonise
Source: Australian Delegation presentation to international forum held in Bonn in May 2012
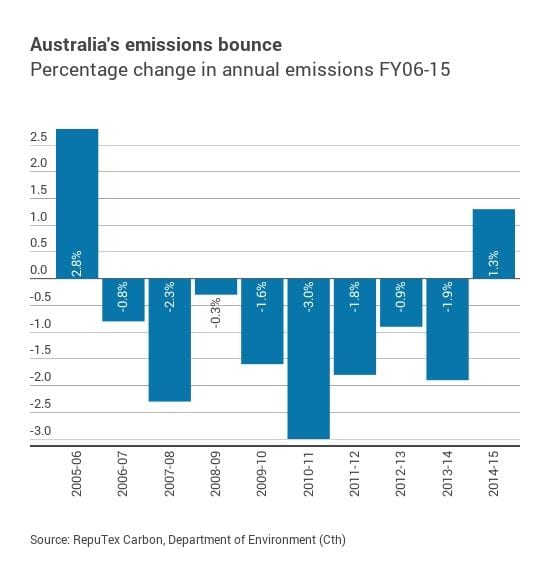
Latest News 2 February 2016, The Guardian, Queensland gives Adani environmental permit for Carmichael coalmine. Huge project clears one more hurdle, but financial uncertainty still hovers over the mine and related rail and port construction at Abbot Point. Adani has secured an environmental permit from the Queensland government to build Australia’s largest coal mine. The Indian conglomerate was issued an environmental authority for its Carmichael mine, west of Bowen in north Queensland, by the department of environment and heritage on Tuesday. It is one less hurdle for Adani’s highly contested plans, after its Australian chief complained last week that delays in government approvals were “incentivising” green activists to plot further legal challenges to stymie the company’s progress. Adani still needs to obtain significant bank funding to realise its $16.5bn mine, rail and port project. It must convince the Queensland government it has obtained “financial closure” before it will be allowed to begin dredging near Great Barrier Reef waters to expand the Abbot Point export facility. A lull in world coal demand and moves in India to rely less on imported thermal coal have cast doubt on the future of the mine. Adani still has to obtain a mining lease from the Queensland government. The state land court last year recommended resources minister Anthony Lynham approve the lease after a legal challenge by conservation group Coast and Country failed to persuade the judge that the mine would have any impact on Asian coal consumption. Read more here 2 February 2016, Climate News Network, Useful waste offers win-win benefits. An unsung success story in the switch to renewable energy is the use of waste to produce gas – and a valuable by-product. The future is increasingly bright for renewable energy, with the US aiming to cut the price of solar photovoltaics by 75%between 2010 and 2020. Denmark plans to obtain 50% of its energy from windjust five years from now. But one form of renewable energy – and one which attracts few headlines – manages to create two useful products at the same time, and is making a growing contribution to combatting climate change. The medieval alchemists who sought to turn base metal into gold would have thrilled at chemistry that let them turn waste into both fuel and fertiliser. Their twenty-first century successors have discovered the secret of doing exactly that. Unwanted food, animal waste, municipal rubbish, crop and forestry residues, sewage and dozens of other left-overs of civilisation can and are now being turned into methane to generate electricity, provide district heating and to fuel road vehicles. Big contribution This largely unheralded revolution takes different forms across the world, mostly because governments set their own rules to encourage the technology, and also because local circumstances provide contrasting piles of waste. But in every case the waste can be converted into gas for use as fuel. Although the technology is only part of the solution to climate change, theEuropean Biogas Association estimates that over time it should be able to replace 30% of current natural gas consumption in Europe. The technology is roughly the same whatever the size of the plant or its location. Biogas plants use microbes to eat waste in an oxygen-free environment to produce methane, and leave fertiliser or soil conditioner as a useful by-product. The plants vary from small household types, very popular in China and India, to farm plants and larger-scale municipal installations in Europe. Read More here 1 February 2016, Renew Economy, Australia emissions surging to record high despite Paris climate deal. Australia’s greenhouse gas emissions are posed to surge to a record high after 2020, and may not reach a peak before 2030 – despite the government’s claim it has been reducing emissions and its support for the Paris climate deal. A new analysis from industry analyst Reputex – a division of global ratings agency Standard & Poor’s – confirms what we already know: despite the Coalition’s rhetoric, emissions in Australia actually rose 1.3 per cent in 2014/15, for the first time since the Coalition was last in power a decade earlier. But the Reputex survey also notes that Australia’s emissions growth is now among the highest in the world, with the government’s own forecast showing emissions will grow 6 per cent to 2020, despite its “Direct Action” plan and the billions spent in the Emissions Reduction Fund. Ironically, the emissions growth would have been faster, but for the fact that Australia’s economic growth has been downgraded sharply from the optimistic assumptions of successive Labor and Coalition governments. Read More here 1 February 2016, WorldWatch Institute, Carbon Trading a hidden threat to soil carbon sequestration? If something has a price tag, people consider its perceived monetary value. But what if, by measuring the value of our planet’s natural systems using dollar amounts alone, we are minimizing their true worth? And what if our focus on solving global problems with money is taking all of us, especially poorer countries, down the wrong road? One global solution to the world’s climate challenges—soil carbon sequestration—may soon face the “threat of the price tag.” A French climate proposal known as the 4 Per 1000 initiative—aimed at increasing the global stock of agricultural soil carbon by 0.4 percent per year on average—attracted worldwide support and media attention when it was officially launched at the December 2015 United Nations climate talks in Paris. The initiative recognizes that good organic agriculture and grazing practices could increase the soil carbon stock and lead to cascading benefits, including improvements in areas such as soil fertility, climate resilience, the nutritional value of foods, and farmers’ livelihoods, all while reversing climate change (see previous Worldwatch blog). But the potential addition of carbon trading—a market-based tool to moderate carbon emissions—into the strategy raises serious concerns.The principles of the 4 Per 1000 initiative will be clarified at a members-only meeting in the first half of 2016, to guide the projects supported by the initiative. As of now, it is unclear whether carbon trading will be part of the design, nor is it known how heavily this initiative will be branded as “a sink for current emissions,” rather than as a true means to reverse already-excessive past emissions in combination with emission-reduction strategies. However, the enthusiasm for carbon pricing at the Paris talks, together with the fact that the initiative’s goal of “0.4 percent annual increase of soil carbon stock” was back-calculated from current fossil fuel emissions (rather than based on the actual potential of soil carbon sequestration), raises serious concerns. Read more here 10 July 2019, Renew Economy : Putin mocks wind turbines, says they shake worms out of the ground. Russia president Vladimir Putin has more in common with US president Donald Trump than we thought: Both have an apparent dislike of wind turbines, and appear believe what is fed to them by some extreme anti-wind blogs. Putin this week chose a manufacturing and industrialisation conference in the industrial city of Yekaterinburg, located in Russia’s most polluted region of Sverdlovsk, to launch an extraordinary attack against wind energy. “Will it be comfortable for people to live on a planet with a palisade of wind turbines and several layers of solar panels?” Putin asked…… At least, however, Putin appears to have changed his tune on the impacts of climate change – at least to a degree. Having previously pointed to the benefits of a warming climate in a country with such a severe winter, Putin’s government now concedes that “global climatic changes are taking place in the world, which have a rather significant effect on economic issues”. It notes that “advanced countries are gradually switching to a low-carbon development model by continuously monitoring and encouraging a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions in various sectors.” Access more here 9 July 2019 Renew Economy: Australia’s emissions surge again, and now well behind Paris trajectory. Australia is falling further behind its Paris emission reduction targets, as the latest emissions estimate from consultancy NDEVR Environmental shows a surge in the first quarter of 2019, increasing the gap between Australia’s emissions and the trajectory that the government insists will be met “in a canter”. In the first three months of 2019, NDEVR estimates in the latest edition of its ‘Tracking 2 Degrees Report’ that Australia’s emissions jumped by 3.4 million tonnes CO2-e compared to the same period a year prior, or around 2.5%. The emissions increase was driven by a substantial increase in electricity emissions, which jumped 8.2%, due to a slight fall in renewable electricity and a rise in fossil fuel generation. NDEVR Environmental track’s Australia’s progress against the emissions reduction targets it has committed to under the Paris Agreement. Its timel and accurate estimates of Australia’s emissions contrasts with the Government’s often late delivery of emissions updates despite orders of Parliament mandating deadlines for their release. The trend shows Australia falling increasingly behind the trajectory needed to achieve its Paris target, which requires Australia to reduce overall emissions through to 2030 by a range of 26% to 28% from 2005 levels. Access more here 7 July 2019, The Guardian: One climate crisis disaster happening every week, UN warns. Climate crisis disasters are happening at the rate of one a week, though most draw little international attention and work is urgently needed to prepare developing countries for the profound impacts, the UN has warned. Catastrophes such as cyclones Idai and Kenneth in Mozambique and the drought afflicting India make headlines around the world. But large numbers of “lower impact events” that are causing death, displacement and suffering are occurring much faster than predicted, said Mami Mizutori, the UN secretary-general’s special representative on disaster risk reduction. “This is not about the future, this is about today.” This means that adapting to the climate crisis could no longer be seen as a long-term problem, but one that needed investment now, she said. “People need to talk more about adaptation and resilience.” Estimates put the cost of climate-related disasters at $520bn a year, while the additional cost of building infrastructure that is resistant to the effects of global heating is only about 3%, or $2.7tn in total over the next 20 years. Read more here 5 July 2019 Climate Home News: Saudi row over 1.5C science raises frustration with UN consensus model. A row over a major scientific report on 1.5C has exposed the limits of the consensus-based approach of the UN climate negotiations. Diplomats privately express growing frustration at tactics used by Saudi Arabia, after the petrostate refused to engage in substantive debate on how best to use the report’s findings to inform climate policies. The obstruction, supported by a handful of other large oil producers, led to the report being excluded from formal negotiation in UN Climate Change’s science stream. That was despite an overwhelming majority of countries calling for a thorough discussion of the topic. One European diplomat described “a toxic political atmosphere” during technical climate talks in Bonn last week, when the row occurred. “We need to be smart about how we use the UN space for political gains to drive ambition,” said the official, who was not authorised to speak on the record, “and not that [a] lack of consensus halts the whole system”. Yvo de Boer, former head of UN Climate Change between 2006 and 2010, vented his outrage on Twitter that “a totalitarian, murderous, sexist regime can exploit consensus rules to block the consideration of science”. Read more here 27 January 2025, Carbon Brief: A record surge of clean energy kept China’s carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions below the previous year’s levels in the last 10 months of 2024. However, the new analysis for Carbon Brief, based on official figures and commercial data, shows the tail end of China’s rebound from zero-Covid in January and February, combined with abnormally high growth in energy demand, stopped CO2 emissions falling in 2024 overall. While China’s CO2 output in 2024 grew by an estimated 0.8% year-on-year, emissions were lower than in the 12 months to February 2024. Other key findings of the analysis include: As ever, the latest analysis shows that policy decisions made in 2025 will strongly affect China’s emissions trajectory in the coming years. In particular, both China’s new commitments under the Paris Agreement and the country’s next five-year plan are being prepared in 2025. Read More Here 3 November 2020, Carbon Brief: Hydrogen gas has long been recognised as an alternative to fossil fuels and a potentially valuable tool for tackling climate change. Now, as nations come forward with net-zero strategies to align with their international climate targets, hydrogen has once again risen up the agenda from Australia and the UK through to Germany and Japan. In the most optimistic outlooks, hydrogen could soon power trucks, planes and ships. It could heat homes, balance electricity grids and help heavy industry to make everything from steel to cement. But doing all these things with hydrogen would require staggering quantities of the fuel, which is only as clean as the methods used to produce it. Moreover, for every potentially transformative application of hydrogen, there are unique challenges that must be overcome. In this in-depth Q&A – which includes a range of infographics, maps and interactive charts, as well as the views of dozens of experts – Carbon Brief examines the big questions around the “hydrogen economy” and looks at the extent to which it could help the world avoid dangerous climate change. Access full article here Fossil fuel emissions have stalled 14 November 2016, The Conversation, Fossil fuel emissions have stalled: Global Carbon Budget 2016. For the third year in a row, global carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels and industry have barely grown, while the global economy has continued to grow strongly. This level of decoupling of carbon emissions from global economic growth is unprecedented.Global CO₂ emissions from the combustion of fossil fuels and industry (including cement production) were 36.3 billion tonnes in 2015, the same as in 2014, and are projected to rise by only 0.2% in 2016 to reach 36.4 billion tonnes. This is a remarkable departure from emissions growth rates of 2.3% for the previous decade, and more than 3% during the 2000’s. Read More here Do you want to understand the complexity of energy systems which support our high consumption lifestyles? Most people don’t give too much thought to where their electricity comes from. Flip a switch, and the lights go on. That’s all. The origins of that energy, or how it actually got into our homes, is generally hidden from view. This link will take you to 11 maps which explain energy in America (it is typical enough as an example of a similar lifestyle as Australia – when I find maps for Oz I’ll add them in) e.g. above map showing the coal plants in the US. Source: Vox Explainers Mapped: how Germany generates its electricity – another example Power to the People – Lock the Gate looks back at the wins of 2015 And there’s lots more coming up in 2016. Some of the big priorities coming up next for the “Lock the Gate” movement are: If you want to give “Lock the Gate” your support – go here for more info This new report reveals that the pollution from Australia’s coal resources, particularly the enormous Galilee coal basin, could take us two-thirds of the way to a two degree rise in global temperature. To Read More and download report The 2006 UK government commissioned Stern Commission Review on the Economics of Climate Change is still the best complete appraisal of global climate change economics. The review broke new ground on climate change assessment in a number of ways. It made headlines by concluding that avoiding global climate change catastrophe was almost beyond our grasp. It also found that the costs of ignoring global climate change could be as great as the Great Depression and the two World Wars combined. The review was (still is) in fact a very good assessment of global climate change, which inferred in 2006 that the situation was a global emergency. Read More here The Garnaut Climate Change Review was commissioned by the Commonwealth, state and territory governments in 2007 to conduct an independent study of the impacts of climate change on the Australian economy. Prof. Garnaut presented The Garnaut Climate Change Review: Final Report to the Australian Prime Minister, Premiers and Chief Ministers in September 2008 in which he examined how Australia was likely to be affected by climate change, and suggested policy responses. In November 2010, he was commissioned by the Australian Government to provide an update to the 2008 Review. In particular, he was asked to examine whether significant changes had occurred that would affect the analysis and recommendations from 2008. The final report was presented May 2011. Since then the Professor has regularly participated in the debate of fossil fuel reduction, as per his latest below: To access his reports; interviews; submissions go here 27 May 2015, Renew Economy, Garnaut: Cost of stranded assets already bigger than cost of climate action. This is one carbon budget that Australia has already blown. Economist and climate change advisor Professor Ross Garnaut has delivered a withering critique of Australia’s economic policies and investment patterns, saying the cost of misguided over-investment in the recent mining boom would likely outweigh the cost of climate action over the next few decades. Read More here Live generation of electricity by fuel type Fossil Fuel Subsidies – The Age of entitlement continues 24 June 2014, Renew Economy, Age of entitlement has not ended for fossil fuels: A new report from The Australia Institute exposes the massive scale of state government assistance, totalling $17.6 billion over a six-year period, not including significant Federal government support and subsidies. Queensland taxpayers are providing the greatest assistance by far with a total of $9.5 billion, followed by Western Australia at $6.2 billion. The table shows almost $18 billion dollars has been spent over the past 6 years by state governments, supporting some of Australia’s biggest, most profitable industries, which are sending most of the profits offshore. That’s $18 billion dollars that could have gone to vital public services such as hospitals, schools and emergency services. State governments are usually associated with the provision of essential services like health and education so it will shock taxpayers to learn of the massive scale of government handouts to the minerals and fossil fuel industries. This report shows that Australian taxpayers have been misled about the costs and benefits of this industry, which we can now see are grossly disproportionate. Each state provides millions of dollars’ worth of assistance to the mining industry every year, with the big mining states of Queensland and Western Australia routinely spending over one billion dollars in assistance annually. Read More here – access full report here What is fossil fuel divestment? Local Governments ready to divest Aligning Council Money With Council Values A Guide To Ensuring Council Money Isn’t Funding Climate Change. 350.org Australia – with the help of the incredible team at Earth Hour – has pulled together a simple 3-step guide for local governments interested in divestment. The movement to align council money with council values is constantly growing in Australia. It complements the existing work that councils are doing to shape a safe climate future. It can also help to reshape the funding practices of Australia’s fossil fuel funding banks. The steps are simple. The impact is huge.The guide can also be used by local groups who are interested in supporting their local government to divest as a step-by-step reference point. Access guide here How coal is staying in the ground in the US Sierra Club Beyond Coal Campaign May 2015, Politico, Michael Grunwald: The war on coal is not just political rhetoric, or a paranoid fantasy concocted by rapacious polluters. It’s real and it’s relentless. Over the past five years, it has killed a coal-fired power plant every 10 days. It has quietly transformed the U.S. electric grid and the global climate debate. The industry and its supporters use “war on coal” as shorthand for a ferocious assault by a hostile White House, but the real war on coal is not primarily an Obama war, or even a Washington war. It’s a guerrilla war. The front lines are not at the Environmental Protection Agency or the Supreme Court. If you want to see how the fossil fuel that once powered most of the country is being battered by enemy forces, you have to watch state and local hearings where utility commissions and other obscure governing bodies debate individual coal plants. You probably won’t find much drama. You’ll definitely find lawyers from the Sierra Club’s Beyond Coal campaign, the boots on the ground in the war on coal. Read More here Oil – conventional & unconventional May 2015, Oil change International Report: On the Edge: 1.6 Million Barrels per Day of Proposed Tar Sands Oil on Life Support. The Canadian tar sands is among the most carbon-intensive, highest-cost sources of oil in the world. Even prior to the precipitous drop in global oil prices late last year, three major projects were cancelled in the sector with companies unable to chart a profitable path forward. Since the collapse in global oil prices, the sector has been under pressure to make further cuts, leading to substantial budget cuts, job losses, and a much more bearish outlook on expansion projections in the coming years. Read full report here. For summary of report USA Sierra Club Beyond Oil Campaign Coal Seam Gas battle in Australia Lock the Gate Alliance is a national coalition of people from across Australia, including farmers, traditional custodians, conservationists and urban residents, who are uniting to protect our common heritage – our land, water and communities – from unsafe or inappropriate mining for coal seam gas and other fossil fuels. Read more about the missions and principles of Lock the Gate. Access more Lock the Gate videos here. Access Lock the Gate fact sheets here 2014: Parliament of Victoria Research Paper: Unconventional Gas: Coal Seam Gas, Shale Gas and Tight Gas: This Research Paper provides an introduction and overview of issues relevant to the development of unconventional gas – coal seam, shale and tight gas – in the Australian and specifically Victorian context. At present, the Victorian unconventional gas industry is at a very early stage. It is not yet known whether there is any coal seam gas or shale gas in Victoria and, if there is, whether it would be economically viable to extract it. A moratorium on fracking has been in place in Victoria since August 2012 while more information is gathered on potential environmental risks posed by the industry. The parts of Victoria with the highest potential for unconventional gas are the Gippsland and Otway basins. Notably, tight gas has been located near Seaspray in Gippsland but is not yet being produced. There is a high level of community concern in regard to the potential impact an unconventional gas industry could have on agriculture in the Gippsland and Otway regions. Industry proponents, however, assert that conventional gas resources are declining and Victoria’s unconventional gas resources need to be ascertained and developed. Read More here 28 January 2015, ABC News, Coal seam gas exploration: Victoria’s fracking ban to remain as Parliament probes regulations: A ban on coal seam gas (CSG) exploration will stay in place in Victoria until a parliamentary inquiry hands down its findings, the State Government has promised. There is a moratorium on the controversial mining technique, known as fracking, until the middle of 2015. The Napthine government conducted a review into CSG, headed by former Howard government minister Peter Reith, which recommended regulations around fracking be relaxed. Labor was critical of the review, claiming it failed to consult with farmers, environmental scientists and local communities. Read more here Keep up to date and how you can be involved here Friends of the Earth Melbourne Coal & Gas Free Victoria 20 May 2015, FoE, Inquiry into Unconventional Gas: Check here for details on the Victorian government’s Inquiry into unconventional gas. The public hearings have not yet started, however the Terms of Reference have been released. The state government’s promised Inquiry into Unconventional Gas has now been formally announced, with broad terms of reference (TOR). FoE’s response to the TOR is available here. The Upper House Environment and Planning Committee will manage the Inquiry. You can find the Inquiry website here. The final TOR will be determined by the committee. Significantly, it is a cross party committee. The Chair is a Liberal (David Davis), and there is one National (Melinda Bath), one Green (Samantha Dunn), three from the ALP (Gayle Tierney, Harriet Shing, Shaun Leane), an additional MP from the Liberals (Richard Dalla-Riva), and one MP from the Shooters Party (Daniel Young). Work started by the previous government, into water tables and the community consultation process run by the Primary Agency, will be released as part of the inquiry.The moratorium on unconventional gas exploration will stay in place until the inquiry delivers its findings. The interim report is due in September and the final report by December. There is the possibility that the committee will amend this timeline if they are overwhelmed with submissions or information. Parliament will then need to consider the recommendations of the committee and make a final decision about how to proceed. This is likely to happen when parliament resumes after the summer break, in early 2016. Quit Coal is a Melbourne-based collective that campaigns against the expansion of the coal and unconventional gas industries in Victoria. Quit Coal uses a range of tactics to tackle this problem. We advise the broader Victorian community about plans for new coal and unconventional gas projects, we put pressure on our government to stop investing in these projects, and we help to inform and mobilise Victorian communities so they can campaign on their own behalf. We focus on being strategic, creative, and as much as possible, fun! The above screen shot is of the Victorian State government’s Mining Licences Near Me site. Go to this link to see what is happening in your area Environment Victoria’s campaign CoalWatch is an interactive resource that tracks the coal industry’s expansion plans and helps builds a movement to stop these polluting developments. CoalWatch provides a way for everyday Victorians to keep track of the coal industry’s ambitious expansion plans. To check what tax-payer money has been pledged to brown coal projects and the coal projects industry is spruiking to our politicians. Here’s another map via EV website (go to their website and you should be able to get better detail from Google Maps: Red areas: Exploration licences (EL). These areas are held by companies to undertake exploration activity. A small bond is held by government in case of any damage. If a company wants to progress the project it needs to obtain a mining licence. Exploration Licence applications are marked with an asterix in the Places Index eg. EL4684*. Yellow areas: Mining Licences (MIN). A mining licence is granted with the expectation that mining will occur. A larger bond is paid to government. Green areas: Exploration licences that have been withdrawn or altered due to community concern. Green outline: Existing mines within Mining Licences. Purple areas: Geological Carbon Storage Exploration areas for carbon capture and storage. On-shore areas have been released by the State Government, while off-shore areas have been released by the Federal Government. The Coal Watch wiki tracks current and future Victorian coal projects, whether they are power stations, coal mines, proposals to export coal or some other inventive way of burning more coal. To get the full picture of coal in Victoria visit our wiki page. Get more info and see the full list of Exploration Licences current at 17 August 2012 here August 2015, Institute for Energy Economics & Financial Analysis – powerpoint: Changing Dynamics in the Global Seaborne Thermal Coal Markets and Stranded Asset Risk. Information from one of the slides follows. To view full presentation go here Economic Implications for Australia 83% of Australian coal mines are foreign owned, hence direct leverage of fossil fuels to the ASX is relatively small at 1-2%. However, for Australia the exposure is high, time is needed for transition and the new industry opportunities are significant: 1. Energy Infrastructure: Australia spends $5-10bn pa on electricity / grid sector, much of it a regulated asset base that all ratepayers fund much of it stranded. BNEF estimate of Australia’s renewable energy infrastructure investment for 2015-2020 was cut 30% from A$20bn post RET. Lost opportunities. 2. Direct employment: The ABS shows a fall of ~20k from the 2012 peak of 70K from coal mining across Australia, and cuts are ongoing. Indirect employment material. 3. Terms of trade: BZE estimates the collapse in the pricing of iron ore, coal and LNG cuts A$100bn pa from Australia’s export revenues by 2030, a halving relative to government budget estimates of 2013/14. Coal was 25% of NSW’s total A$ value of exports in 2013/14 (38% of Qld). Australia will be #1 globally in LNG by 2018. 4. The financial sector: is leveraged to mining and associated rail port infrastructure. WICET 80% financed by banks, mostly Australian. Adani’s Abbot Point Port is foreign owned, but A$1.2bn of Australian sourced debt. Insurance firms and infrastructure funds are leveraged to fossil fuels vs little RE infrastructure assets. BBY! 5. Rehabilitation: $18bn of unfunded coal mining rehabilitation across Australia. 6. Economic growth: curtailed as Australia fails to develop low carbon industries. Analysis: Record surge of clean energy in 2024 halts China’s CO2 rise

In-depth Q&A: Does the world need hydrogen to solve climate change?
 3 May 2016, Carbon Brief, The global coal trade doubled in the decade to 2012 as a coal-fueled boom took hold in Asia. Now, the coal trade seems to have stalled, or even gone into reverse. This change of fortune has devastated the coal mining industry, with Peabody – the world’s largest private coal-mining company – the latest of 50 US firms to file for bankruptcy. It could also be a turning point for the climate, with the continued burning of coal the biggest difference between business-as-usual emissions and avoiding dangerous climate change. Carbon Brief has produced a series of maps and interactive charts to show how the global coal trade is changing. As well as providing a global overview, we focus on a few key countries: Read More here
3 May 2016, Carbon Brief, The global coal trade doubled in the decade to 2012 as a coal-fueled boom took hold in Asia. Now, the coal trade seems to have stalled, or even gone into reverse. This change of fortune has devastated the coal mining industry, with Peabody – the world’s largest private coal-mining company – the latest of 50 US firms to file for bankruptcy. It could also be a turning point for the climate, with the continued burning of coal the biggest difference between business-as-usual emissions and avoiding dangerous climate change. Carbon Brief has produced a series of maps and interactive charts to show how the global coal trade is changing. As well as providing a global overview, we focus on a few key countries: Read More here/cdn0.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/3915730/EIA%20coal%20power%20plants.png)

21 April 2015, Climate Council, Will Steffen: Unburnable Carbon: Why we need to leave fossil fuels in the ground.Stern Commission Review
Australia’s Garnaut Review
 November 2014 – The Fossil Fuel Bailout: G20 subsidies for oil, gas and coal exploration report: Governments across the G20 countries are estimated to be spending $88 billion every year subsidising exploration for fossil fuels. Their exploration subsidies marry bad economics with potentially disastrous consequences for climate change. In effect, governments are propping up the development of oil, gas and coal reserves that cannot be exploited if the world is to avoid dangerous climate change. This report documents, for the first time, the scale and structure of fossil fuel exploration subsidies in the G20 countries. The evidence points to a publicly financed bailout for carbon-intensive companies, and support for uneconomic investments that could drive the planet far beyond the internationally agreed target of limiting global temperature increases to no more than 2ºC. It finds that, by providing subsidies for fossil fuel exploration, the G20 countries are creating a ‘triple-lose’ scenario. They are directing large volumes of finance into high-carbon assets that cannot be exploited without catastrophic climate effects. They are diverting investment from economic low-carbon alternatives such as solar, wind and hydro-power. And they are undermining the prospects for an ambitious climate deal in 2015. Access full report here For the summary on Australia’s susidisation of it’s fossil fuel industry go to page 51 of the report. The report said that the United States and Australia paid the highest level of national subsidies for exploration in the form of direct spending or tax breaks. Overall, G20 country spending on national subsidies was $23 billion. In Australia, this includes exploration funding for Geoscience Australia and tax deductions for mining and petroleum exploration. The report also classifies the Federal Government’s fuel rebate program for resources companies as a subsidy.
November 2014 – The Fossil Fuel Bailout: G20 subsidies for oil, gas and coal exploration report: Governments across the G20 countries are estimated to be spending $88 billion every year subsidising exploration for fossil fuels. Their exploration subsidies marry bad economics with potentially disastrous consequences for climate change. In effect, governments are propping up the development of oil, gas and coal reserves that cannot be exploited if the world is to avoid dangerous climate change. This report documents, for the first time, the scale and structure of fossil fuel exploration subsidies in the G20 countries. The evidence points to a publicly financed bailout for carbon-intensive companies, and support for uneconomic investments that could drive the planet far beyond the internationally agreed target of limiting global temperature increases to no more than 2ºC. It finds that, by providing subsidies for fossil fuel exploration, the G20 countries are creating a ‘triple-lose’ scenario. They are directing large volumes of finance into high-carbon assets that cannot be exploited without catastrophic climate effects. They are diverting investment from economic low-carbon alternatives such as solar, wind and hydro-power. And they are undermining the prospects for an ambitious climate deal in 2015. Access full report here For the summary on Australia’s susidisation of it’s fossil fuel industry go to page 51 of the report. The report said that the United States and Australia paid the highest level of national subsidies for exploration in the form of direct spending or tax breaks. Overall, G20 country spending on national subsidies was $23 billion. In Australia, this includes exploration funding for Geoscience Australia and tax deductions for mining and petroleum exploration. The report also classifies the Federal Government’s fuel rebate program for resources companies as a subsidy.