2 February 2016, The Guardian, Queensland gives Adani environmental permit for Carmichael coalmine. Huge project clears one more hurdle, but financial uncertainty still hovers over the mine and related rail and port construction at Abbot Point. Adani has secured an environmental permit from the Queensland government to build Australia’s largest coal mine. The Indian conglomerate was issued an environmental authority for its Carmichael mine, west of Bowen in north Queensland, by the department of environment and heritage on Tuesday. It is one less hurdle for Adani’s highly contested plans, after its Australian chief complained last week that delays in government approvals were “incentivising” green activists to plot further legal challenges to stymie the company’s progress. Adani still needs to obtain significant bank funding to realise its $16.5bn mine, rail and port project. It must convince the Queensland government it has obtained “financial closure” before it will be allowed to begin dredging near Great Barrier Reef waters to expand the Abbot Point export facility. A lull in world coal demand and moves in India to rely less on imported thermal coal have cast doubt on the future of the mine. Adani still has to obtain a mining lease from the Queensland government. The state land court last year recommended resources minister Anthony Lynham approve the lease after a legal challenge by conservation group Coast and Country failed to persuade the judge that the mine would have any impact on Asian coal consumption. Read more here
Category Archives: The Mitigation Battle
2 February 2016, Climate News Network, Useful waste offers win-win benefits. An unsung success story in the switch to renewable energy is the use of waste to produce gas – and a valuable by-product. The future is increasingly bright for renewable energy, with the US aiming to cut the price of solar photovoltaics by 75%between 2010 and 2020. Denmark plans to obtain 50% of its energy from windjust five years from now. But one form of renewable energy – and one which attracts few headlines – manages to create two useful products at the same time, and is making a growing contribution to combatting climate change. The medieval alchemists who sought to turn base metal into gold would have thrilled at chemistry that let them turn waste into both fuel and fertiliser. Their twenty-first century successors have discovered the secret of doing exactly that. Unwanted food, animal waste, municipal rubbish, crop and forestry residues, sewage and dozens of other left-overs of civilisation can and are now being turned into methane to generate electricity, provide district heating and to fuel road vehicles. Big contribution This largely unheralded revolution takes different forms across the world, mostly because governments set their own rules to encourage the technology, and also because local circumstances provide contrasting piles of waste. But in every case the waste can be converted into gas for use as fuel. Although the technology is only part of the solution to climate change, theEuropean Biogas Association estimates that over time it should be able to replace 30% of current natural gas consumption in Europe. The technology is roughly the same whatever the size of the plant or its location. Biogas plants use microbes to eat waste in an oxygen-free environment to produce methane, and leave fertiliser or soil conditioner as a useful by-product. The plants vary from small household types, very popular in China and India, to farm plants and larger-scale municipal installations in Europe. Read More here
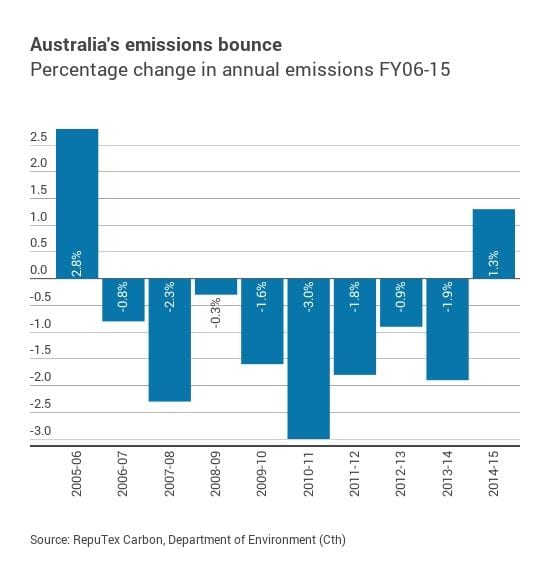
1 February 2016, Renew Economy, Australia emissions surging to record high despite Paris climate deal. Australia’s greenhouse gas emissions are posed to surge to a record high after 2020, and may not reach a peak before 2030 – despite the government’s claim it has been reducing emissions and its support for the Paris climate deal. A new analysis from industry analyst Reputex – a division of global ratings agency Standard & Poor’s – confirms what we already know: despite the Coalition’s rhetoric, emissions in Australia actually rose 1.3 per cent in 2014/15, for the first time since the Coalition was last in power a decade earlier.
But the Reputex survey also notes that Australia’s emissions growth is now among the highest in the world, with the government’s own forecast showing emissions will grow 6 per cent to 2020, despite its “Direct Action” plan and the billions spent in the Emissions Reduction Fund. Ironically, the emissions growth would have been faster, but for the fact that Australia’s economic growth has been downgraded sharply from the optimistic assumptions of successive Labor and Coalition governments. Read More here
1 February 2016, WorldWatch Institute, Carbon Trading a hidden threat to soil carbon sequestration? If something has a price tag, people consider its perceived monetary value. But what if, by measuring the value of our planet’s natural systems using dollar amounts alone, we are minimizing their true worth? And what if our focus on solving global problems with money is taking all of us, especially poorer countries, down the wrong road? One global solution to the world’s climate challenges—soil carbon sequestration—may soon face the “threat of the price tag.” A French climate proposal known as the 4 Per 1000 initiative—aimed at increasing the global stock of agricultural soil carbon by 0.4 percent per year on average—attracted worldwide support and media attention when it was officially launched at the December 2015 United Nations climate talks in Paris. The initiative recognizes that good organic agriculture and grazing practices could increase the soil carbon stock and lead to cascading benefits, including improvements in areas such as soil fertility, climate resilience, the nutritional value of foods, and farmers’ livelihoods, all while reversing climate change (see previous Worldwatch blog). But the potential addition of carbon trading—a market-based tool to moderate carbon emissions—into the strategy raises serious concerns.The principles of the 4 Per 1000 initiative will be clarified at a members-only meeting in the first half of 2016, to guide the projects supported by the initiative. As of now, it is unclear whether carbon trading will be part of the design, nor is it known how heavily this initiative will be branded as “a sink for current emissions,” rather than as a true means to reverse already-excessive past emissions in combination with emission-reduction strategies. However, the enthusiasm for carbon pricing at the Paris talks, together with the fact that the initiative’s goal of “0.4 percent annual increase of soil carbon stock” was back-calculated from current fossil fuel emissions (rather than based on the actual potential of soil carbon sequestration), raises serious concerns. Read more here