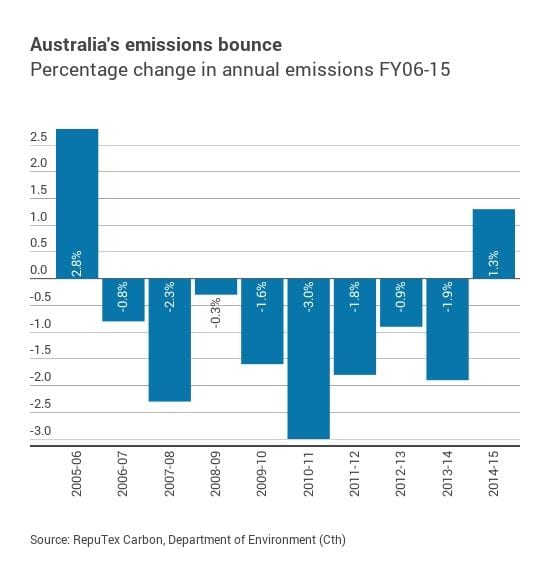
1 February 2016, Renew Economy, Australia emissions surging to record high despite Paris climate deal. Australia’s greenhouse gas emissions are posed to surge to a record high after 2020, and may not reach a peak before 2030 – despite the government’s claim it has been reducing emissions and its support for the Paris climate deal. A new analysis from industry analyst Reputex – a division of global ratings agency Standard & Poor’s – confirms what we already know: despite the Coalition’s rhetoric, emissions in Australia actually rose 1.3 per cent in 2014/15, for the first time since the Coalition was last in power a decade earlier.
But the Reputex survey also notes that Australia’s emissions growth is now among the highest in the world, with the government’s own forecast showing emissions will grow 6 per cent to 2020, despite its “Direct Action” plan and the billions spent in the Emissions Reduction Fund. Ironically, the emissions growth would have been faster, but for the fact that Australia’s economic growth has been downgraded sharply from the optimistic assumptions of successive Labor and Coalition governments. Read More here